[Lecture Notes] ShanghaiTech EE111 Digital Circuits
Topic 1. Intro to digital fundamentals
Asynchronous(异步) / Synchronous(同步) circuits
本课不涉及异步电路, handshaking 非常复杂.
Topic 2. Number systems, operations and codes
BCD (binary coded decimal)
- represents each decimal digit with a 4-bit code
- commonly used when it’s necessary to show decimal numbers like clocks
Gray code
- only a single bit change between one code world
- can avoid problems in where an error may occur when >1 bit changes at a time
- (from right) 1st digit: 0110; 2nd digit: 00111100, …
- Race condition (竞争-冒险现象)
Topic 3. Logic gates
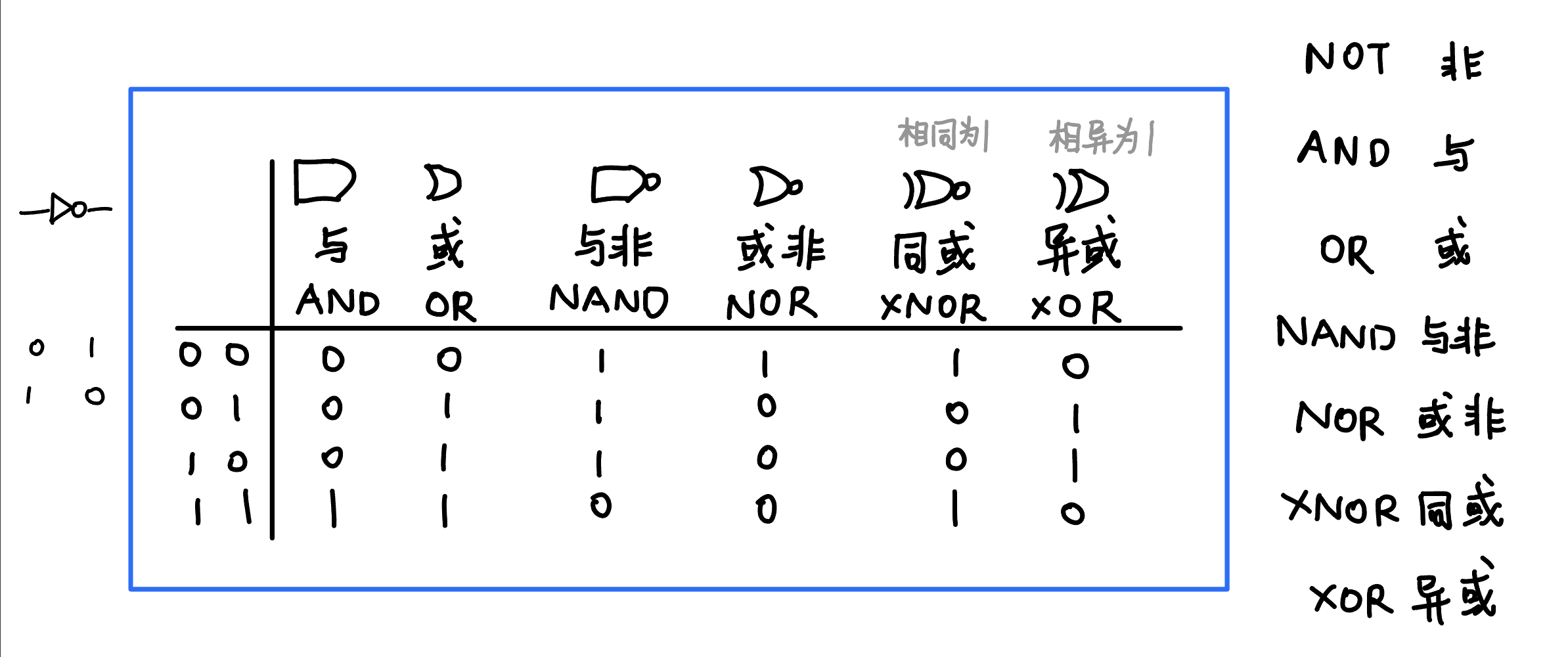
Topic 5. Bool algebra & logic simplification
Boolean Algebra
Commutative laws: ;
Associative laws: ;
Distributive law:
Rules of boolean algebra

DeMorgan’s 1st Theorem:
DeMorgan’s 2nd Theorem:
SOP & POS
SOP (sum-of-products)
In SOP, every variable must appear in each term. (每个变量在每一项中都必须出现)
e.g.
最小项(之和)
是乘积项,是变量个数
对于变量函数,有个最小项
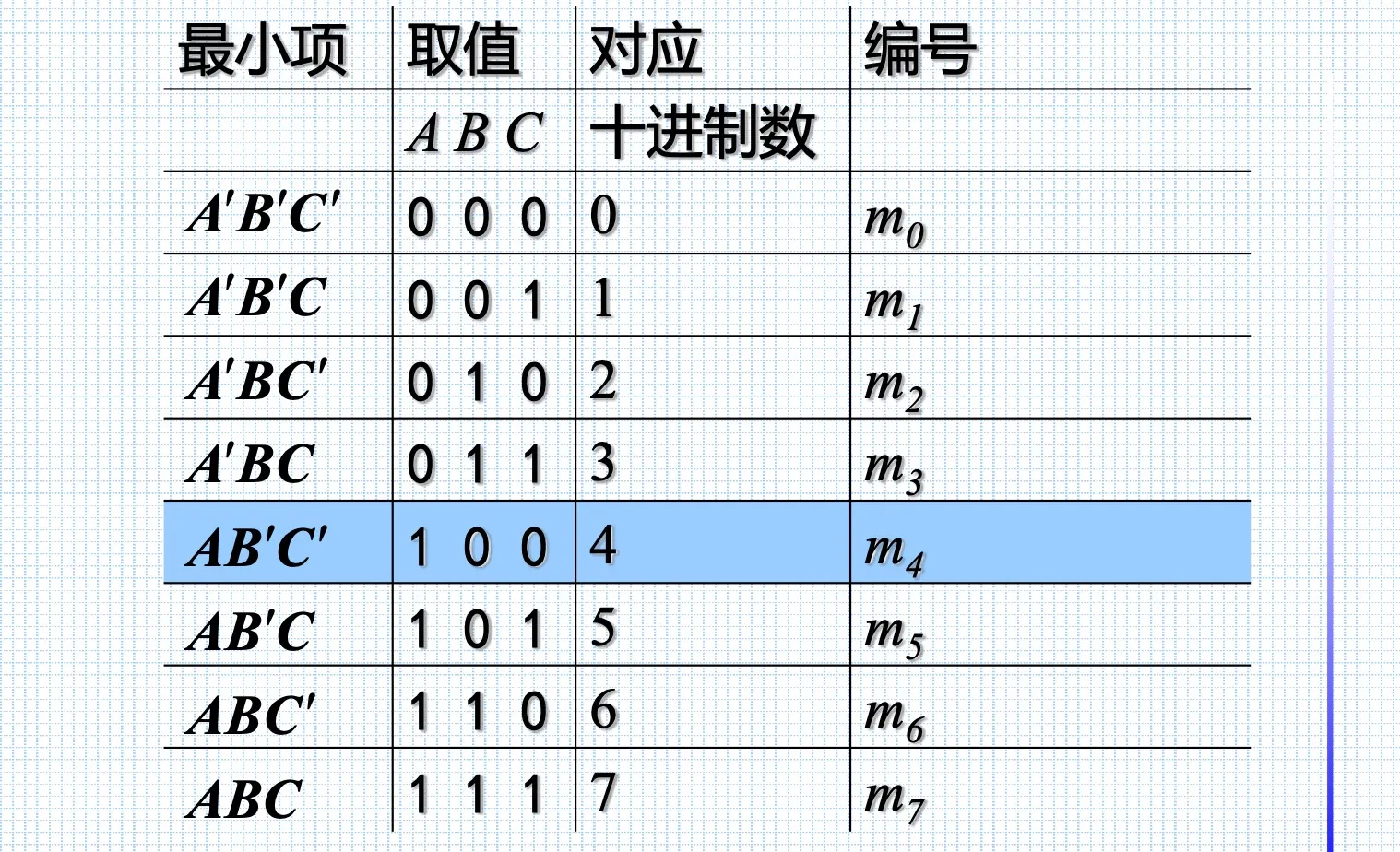
性质:
任意输入变量的取值,仅有一个最小项值为1
全体最小项之和为1
任意两最小项之积为0
利用,两个**相邻(adjacent)**最小项之和可以合并
e.g.
最大项(之积)
是相加项,包含个因子
对于变量函数,有个最大项
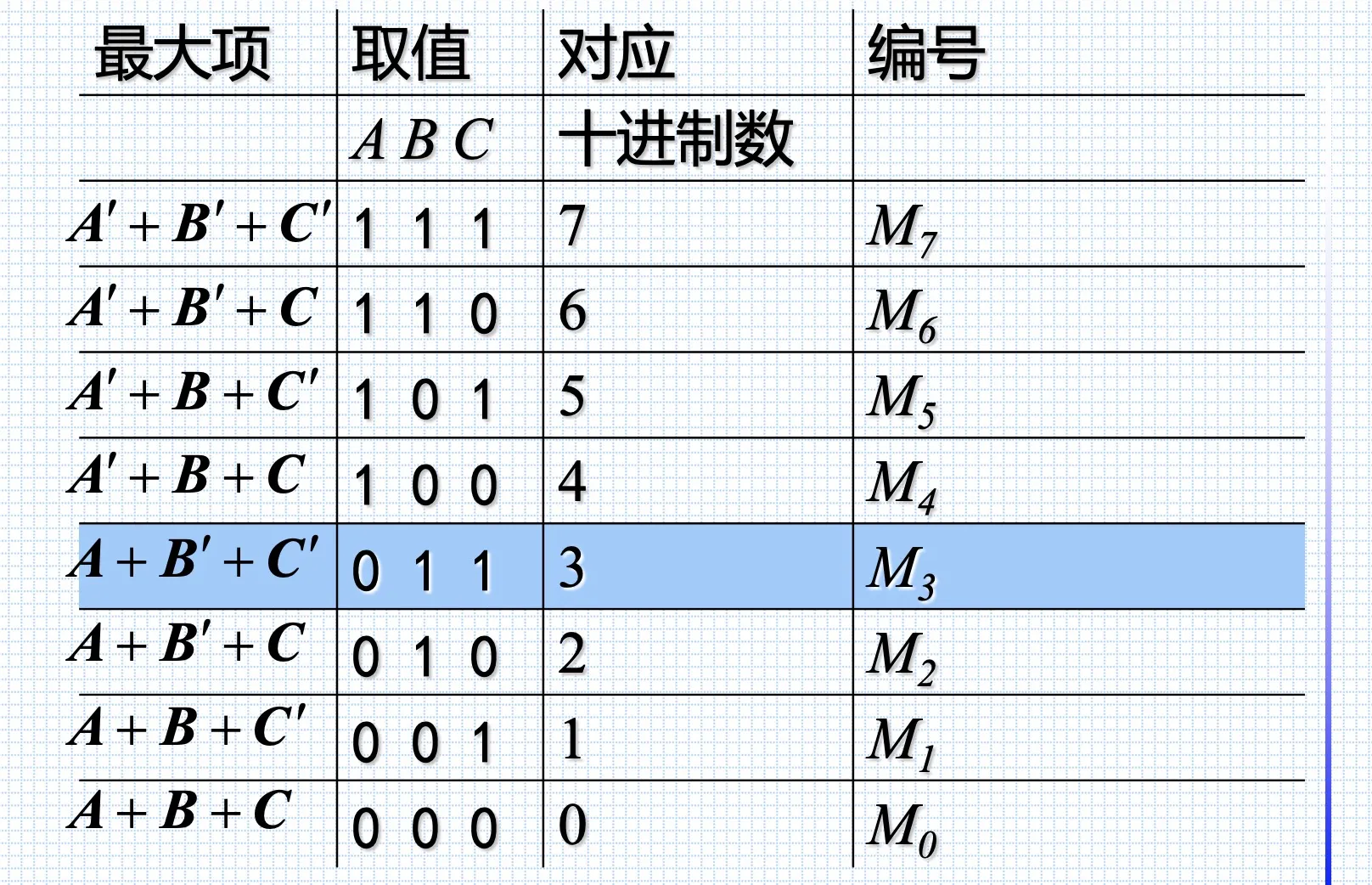
性质:
- 任意输入变量的取值,仅有一个最大项值为1
- 全体最大项之积为0
- 任意两最大项之和为1
- 只有一个变量不同的最大项的乘积等于各相同变量之和
Karnaugh Maps 卡诺图
用卡诺图转 standard SOP
Place a ‘1’ for each minterm
将每个1写成product形式(e.g. )
卡诺图转 non standard SOP
Expand product terms to minterms and place ‘1’ for each minterm
e.g.
Mapping a standard POS expression
Place a ‘0’ for each maxterm.
Quine-McCluskey Method
Variable: the input
Literal: a variable complemented or uncomplemented
Implicant: a product term of literals obtained from K-map such that when implicant = 1, F = 1
Prime Implicant (PI): the implicant that cannot be further simplified
Essential Prime Implicant (EPI): The PI which contain 1’s that can only be grouped in this way
Cover: a set of prime implicants which covers all 1s
Chapter 5. Combinational Logic analysis
AND-OR logic
AND-OR-Invert logic
将 AND-OR 中 0和1反过来, 整体加上一个非
NAND-only
在 AND-OR 基础上, 加上两层非, 使用
NOR-only
在 AOI 基础上, 使用 $\overline{A} \cdot \overline{B} = \overline{A+B} $
加圈代表是low-active
Combinational logic 组合逻辑
组合逻辑: 任意时刻的输出仅依赖当前时刻的输入
Chapter 7. VHDL
VHDL: very high speed integrated circuits hardware description language
FPGA: field programmable gate array
VHDL language
1 | |
Entity: port mode
<mode>: IN, OUT, BUFFER(只能一个输入), INOUT (可以由多个source更改)
Architecture: one possible implementation of its associated entity
- architecture declarations: 定义局部的signal, components变量
- signal定义;component定义;constant定义;type定义;attribute定义
- architecture body: 定义实现
- concurrent assignment statements 并行的赋值语句 (WITH SELECT WHEN; WHEN ELSE)
- component instantiation statements
- process statements (sequential 顺序的赋值语句 WAIT IF CASE LOOP)
- generate statements
- architecture declarations: 定义局部的signal, components变量
VHDL is concurrent 并行结构,改变顺序不影响电路功能
多个PROCESS之间是并行的,单个PROCESS里面的语句是顺序执行的,改变顺序会改变功能
当PROCESS的sensitivity list中有信号改变时,PROCESS里的语句会被顺序执行
运算符优先级(由高到低)
- NOT, abs, ** (指数)
- *乘, /除, mod取模, rem取余
- +, - 正负号
- +, -, & 加减法
- sll, srl, sla, sra, rol, ror 移位
- =, /=, <, <=, >, >=
- AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR 逻辑运算符
Chapter 8. Sequential Circuits 时序电路
Latches
Latch 能存储1bit的信息
Basic SR latch
S和R都是 active high 信号
S和R都是1的时候状态不定
可以用两个NOR实现,也可以用两个NAND实现,用NAND实现的时候是active low
Gated SR latch
Clk=0的时候保持上一状态, Clk=1的时候相当于basic SR latch
可以用AND和NOR,也可以用NAND(NAND更好)
Gated D latch
Clk=0的时候保持上一状态, Clk=1的时候跟随输入D
1 | |
- level sensitive circuits
- 当clock为active的时候,output将保持变化,可能会变化多次
- Gated SR latch, Gated D latch都属于此类,但basic SR latch不属于,因为它没有clk
- level triggered circuit
- 包括 latch (basic SR latch)
Flip-flops
D flip-flop
在active clock edge的时候output跟随input
- Master-slave D flip-flop (使用两个D latch做成)
- Edge triggered D flip-flop
1 | |
T flip-flop
T=0时保持状态, T=1时反转状态
JK flip-flop
如果把J和K合二为一,相当于T flip-flop
如果J和K不同时为1,相当于SR-latch (basic SR latch不能输入同时为1)
Registers
N-bit register
由N个flip-flop组成,能存储N个bit
Shift register 移位寄存器
Input is shifted to the right by one bit during each clock cycle
移位寄存器类型
- Serial-in serial-out (SISO)
- Serial-in parallel-out
- Parallel-in serial-out
- Parallel-in parallel-out
Counters
Chapter 9. Synchronous sequential Circuits
Sequential circuits 的两种类型
- Moore: output仅与state有关
- Mealy: output与state和input都有关
State diagram / State table
每个state用一组state variables表示,每个state variable可以用一个flip-flop实现。
One-hot encoding: state的数量与state variable的数量相同